Scalable Self-Hosted GitHub Runners on AWS Cloud
This post describes the procedure for implementing the Github-EventBridge partner integration using a Python-based Lambda with an in-built HTTPs public endpoint (Function URL)—to be used as the payload URL during the GitHub webhook configuration.
The process for generating a “blueprint” deployment has been streamlined via a Quickstart Cloudformation template.
Prerequisites
- An Event Bus has been created in Amazon EventBridge
- Understanding of concepts published by Github in relation webhook best practices
Create Webhook Secret
Generate a secret with sufficient entropy.
$ echo `hexdump -n 32 /dev/urandom -v -e '"" 1/1 "%02X" ""'`sample output:
F379CE1F3736FE95803EBE669AAB77170712DC7B3D146078BE898EB8A784FA7EDeploy GitHub-EventBridge Integration using CloudFormation
The following approaches for deployment are covered:
- AWS Console
- AWS SAM
AWS Console
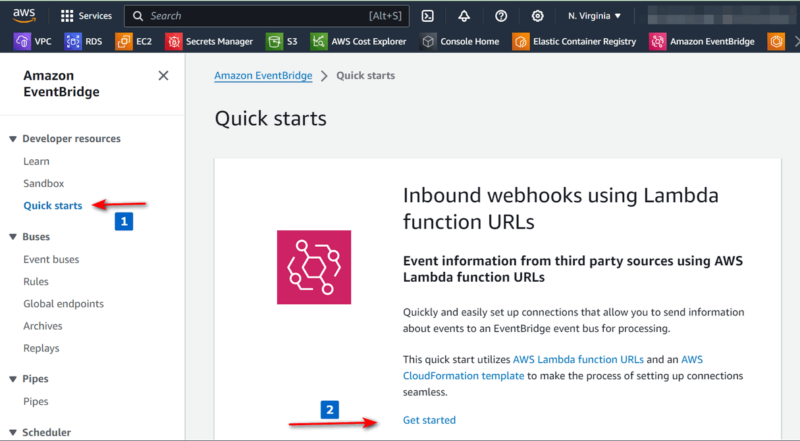
Start by following the guided setup at:
- “Amazon EventBridge”
->“Quick starts”->“Inbound webhooks using Lambda function URLs”->“Get started”
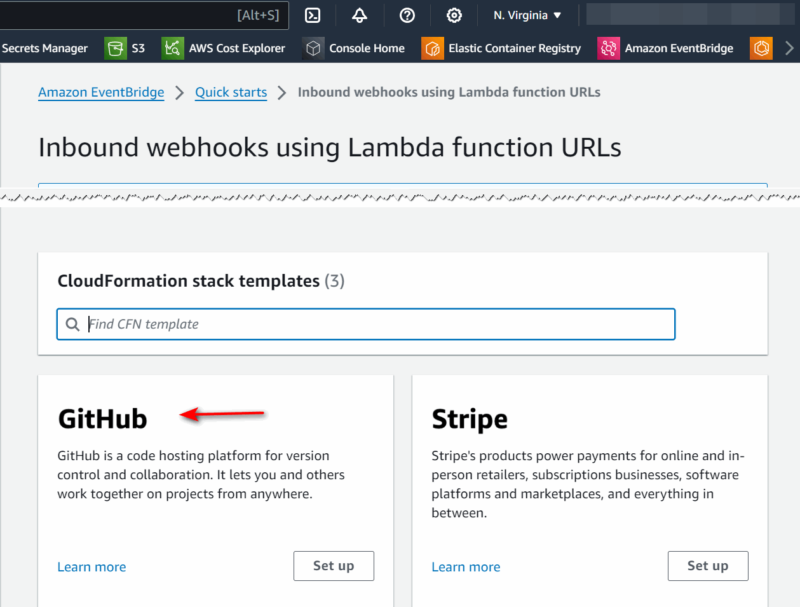
- from the list of “CloudFormation stack templates“, locate the “GitHub“, and click “Set up“
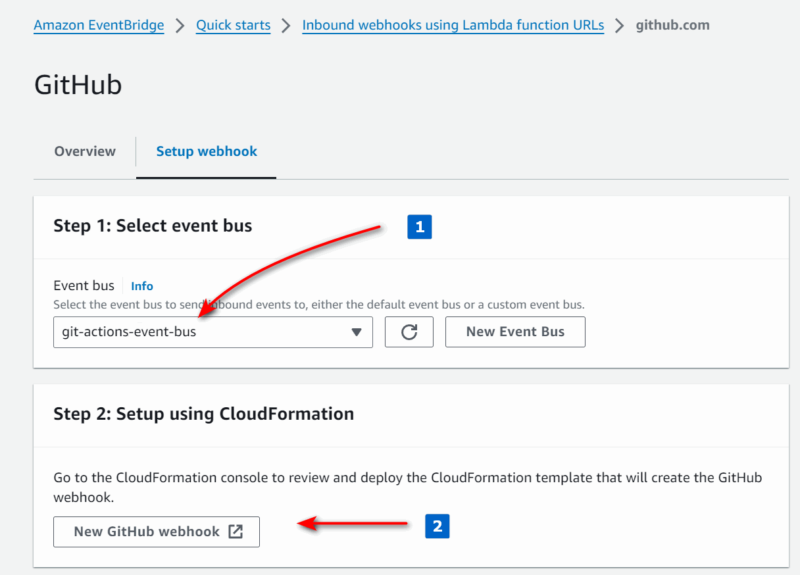
- choose the Event Bus which should receive the GitHub events, then click on “New Github webhook“
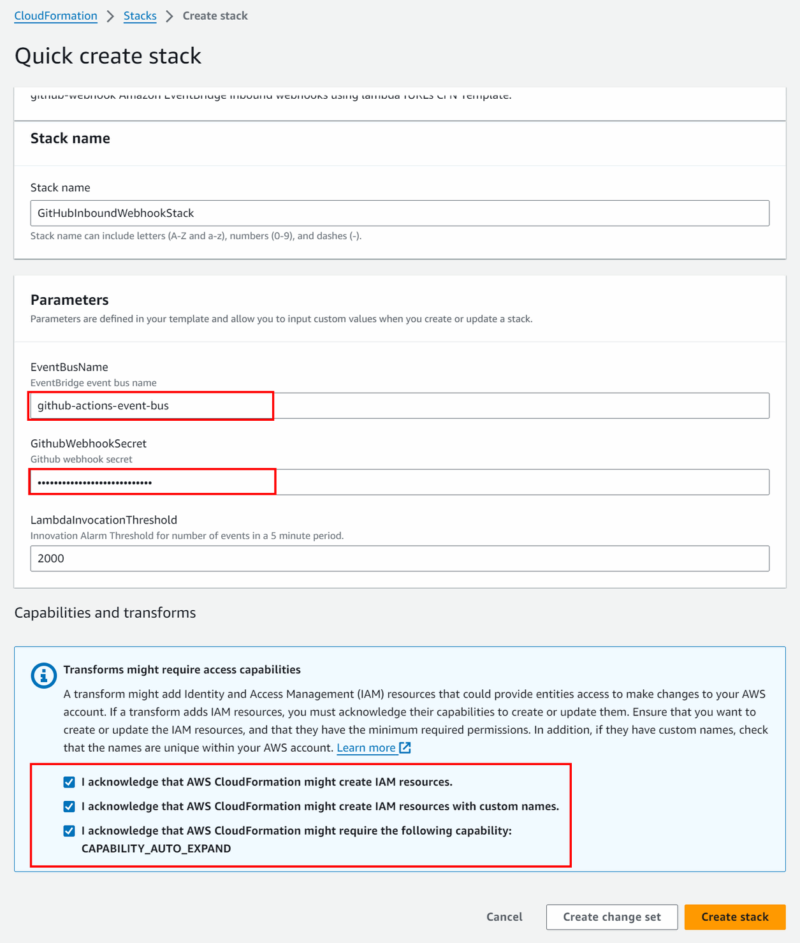
- accept the prompt, requesting you acknowledge/accept a publically accessible URL will be created
- note: the Lambda performs signature validation using the secret and payload
- consider using Amazon Cognito, Amazon CloudFront and AWS WAF to further enhance the security of public function URLs
- provide a Stack name, the Eventbus name and Github webhook secret, as generated in “Create Webhook Secret“
- click on “Create stack” to allow Cloudformation to generate the stack and initiate the deployment of resources
- deployment can be monitored by visiting “CloudFormation”
->“Stack”->“<stack name>” - review the “Outputs” and “Resources” created by the stack
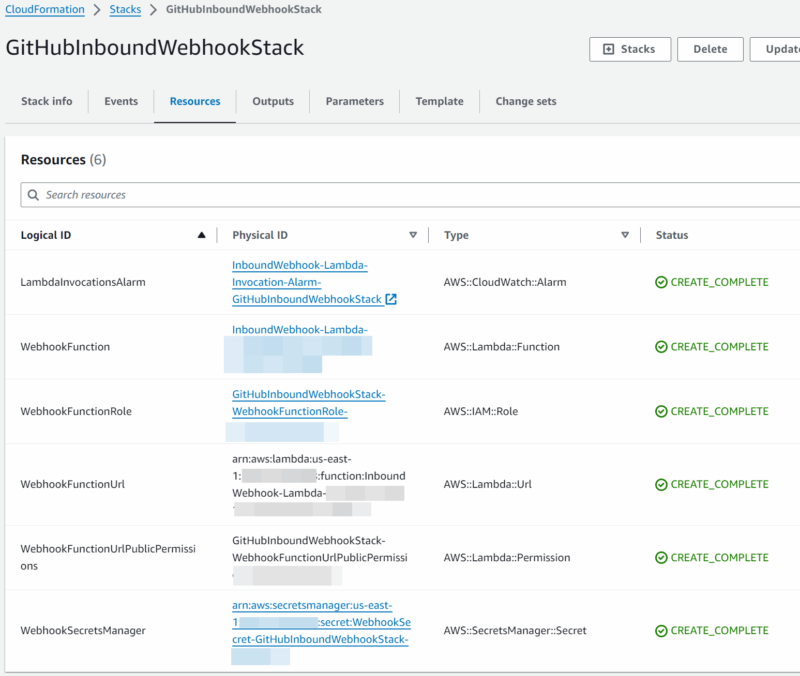
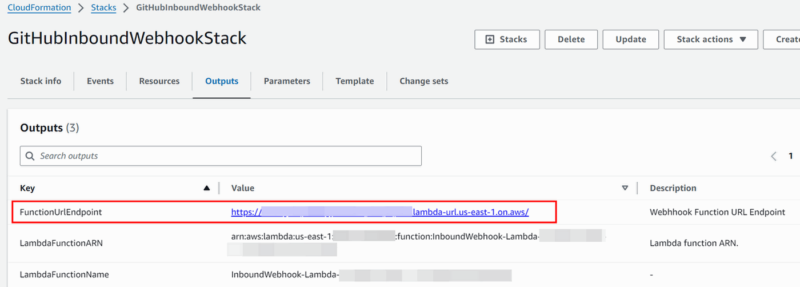
- make a note of the FunctionUrlEndpoint (and webhook secret used during the setup)
- these will be used during the configuration of the GitHub Organization webhook
AWS SAM
Using this approach provides a greater appreciation of the Lambda code/resources that make up the integration.
The following git repository contains a CloudFormation project which supports parameter-driven resource names for deploying the integration using AWS SAM.
https://github.com/tonys-code-base/git-actions-webhook-cf.git
