GitHub code scanning of private repositories with CodeQL, is only available for organizations that have purchased the GitHub Advanced Security License.
If you don’t own a license, you can still use CodeQL to perform scans against public repositories.
This post covers the following:
- Creating a public test repository (with source code vulnerabilities) within a GitHub organization
- Configure the organization settings to allow workflows within the repository to be executed on a self-hosted runner
- Create a workflow to perform a CodeQL scan against the repository contents, and upload results to GitHub
- Viewing the uploaded code scan results
Configure GitHub Organization
If you need to create a new organization, refer to the available plan options.
To configure an existing organization:
- Display the list of organizations within your account
- Choose
"Settings"for the target organization and configure as outlined in the points below

Actions -> General -> "Fork pull request workflows from outside collaborators”- Choose option: “
Require approval for all outside collaborators“
- Choose option: “
Actions -> Runner Groups -> Default"Repository access"->"All repositories"- Ensure “
Allow public repositories” is ticked/selected
- Ensure “
"Workflow access"->"All workflows"
- repository/workflow access can be refined/hardened after creation of our test repository
Create Test Repository
A sample test repository can be found at https://github.com/GitHubSecurityLab/codeql-zero-to-hero. The repository was created by GitHubSecurityLab.
- Import/upload a copy of the above repo to your target GitHub organization
Spawn Self-Hosted Runner
- Launch an organization-level self-hosted runner by navigating to:
"Actions -> Runners -> New Runner“
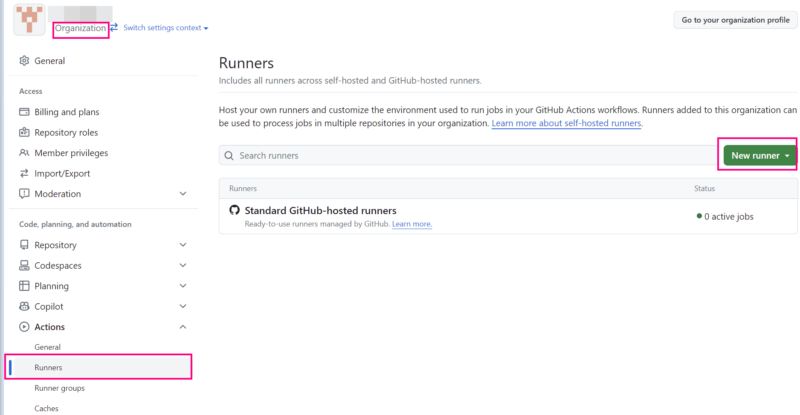
- During the runner installation/configuration process, choose the following:
runner group: Defaultrunner name: codescanadditional labels: codescan- all other options, choose the default settings
# Runner Registration
Enter the name of the runner group to add this runner to: [press Enter for Default]
Enter the name of runner: [press Enter for ***] codescan
This runner will have the following labels: 'self-hosted', 'Linux', 'X64'
Enter any additional labels (ex. label-1,label-2): [press Enter to skip] codescan
Enter any additional labels (ex. label-1,label-2): [press Enter to skip]
...
...
Enter name of work folder: [press Enter for _work]
√ Settings Saved.CodeQL Workflow for Code Scanning
- Create the following workflow
<repo root>/.github/workflows/codeql.yml
name: "CodeQL"
on:
push:
branches: [ main ]
permissions:
actions: read
contents: read
security-events: write
jobs:
analyze:
name: Analyze
runs-on: codescan
steps:
- name: Checkout repository
uses: actions/checkout@v3
# Initializes the CodeQL tools for scanning.
- name: Initialize CodeQL
uses: github/codeql-action/init@v3
# If you wish to specify custom queries, you can do so here or in a config file.
# By default, queries listed here will override any specified in a config file.
# Prefix the list here with "+" to use these queries and those in the config file.
# queries: ./path/to/local/query, your-org/your-repo/queries@main
# Autobuild attempts to build any compiled languages (C/C++, C#, or Java).
# If this step fails, then you should remove it and run the build manually (see below)
- name: Autobuild
uses: github/codeql-action/autobuild@v3
# ℹ️ Command-line programs to run using the OS shell.
# 📚 https://git.io/JvXDl
# ✏️ If the Autobuild fails above, remove it and uncomment the following three lines
# and modify them (or add more) to build your code if your project
# uses a compiled language
#- run: |
# make bootstrap
# make release
- name: Perform CodeQL Analysis
uses: github/codeql-action/analyze@v3
- The workflow was derived using information/code sourced from the following links:
- Commit/push changes to remote target
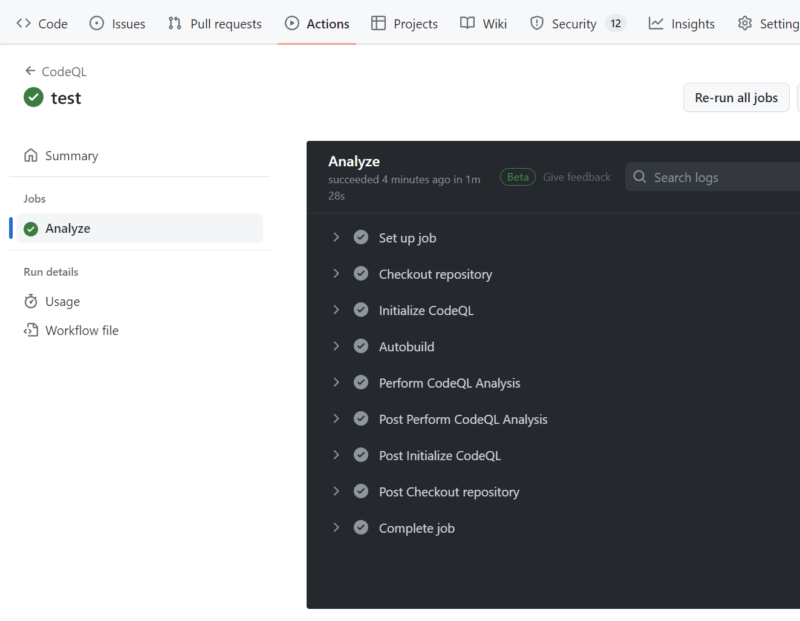
- Monitor the workflow via the repository
Actionsmenu
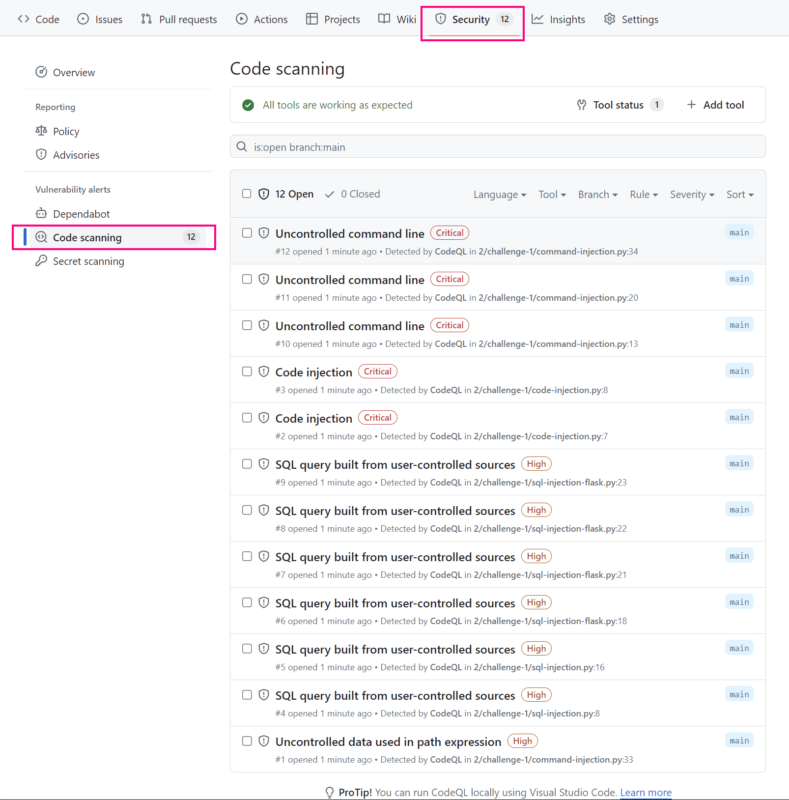
- Once the workflow completes, choose
Security -> Code scanningto view the results of the code scan